
by editor | Dec 10, 2024 | Clinical Compliance, Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Human Resources, Keys to Compassionate Care, Regulatory Compliance
When an employee brings forward a compliance concern, they’re engaging in what the law defines as protected activity. This might involve reporting a potential violation of hospice regulations, concerns about Medicare fraud, or even raising issues about unsafe working conditions. These are rights guaranteed under various laws, like the False Claims Act, OSHA protections, and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, which protect employees who speak up.
In responding to employee concerns, there is a fine line between addressing workplace concerns and crossing into retaliation territory. Retaliation isn’t always a blatant act of revenge. Sometimes, it’s more subtle, even subconscious. Sometimes management at the hospice agency may feel frustrated or betrayed by an employee’s complaint and – without realizing it – allow those feelings to influence their decisions. Maybe the employee was already struggling with performance, or maybe there were pre-existing tensions on the team. But when an adverse action—like firing, demotion, or cutting hours—happens shortly after a complaint, it’s easy for that decision to be seen as retaliatory, even if it wasn’t intended that way.
What is Retaliation?
To clarify what retaliation means, it’s any adverse action taken against an employee because they engaged in protected activity. Timing is a major red flag here. If an employee files a compliance report and is terminated shortly after, it raises questions. Even if you feel justified in your decision, the timing alone can look suspect to a court, regulatory agency, or even the employee’s peers.
What are the Consequences of Retaliation
And the consequences for retaliation? They’re not just legal—they’re also reputational. If a claim is brought against an agency, the agency could face:
- Reinstatement of the employee to their position, even if you’ve moved on.
- Back pay, damages, and legal fees, which can quickly add up.
- Regulatory scrutiny, which might open the door to deeper investigations into the agency’s practices.
- And, perhaps most damaging, the perception that we don’t care about compliance or employee rights. That’s not a message we can afford to send.
From the employee’s perspective, they have a number of options if they feel they’ve been retaliated against. They might file a complaint with OSHA, EEOC, or state regulators. They could seek legal action for wrongful termination or take their concerns to external auditors or even the media. Once that door is opened, the hospice agency loses control of the narrative.
How Can You Avoid Retaliatory Behavior?
So, what can you do to avoid even the appearance of retaliation? Here’s are some suggestions:
- Document everything: If there are performance concerns or other issues unrelated to the complaint, make sure there’s a clear, consistent record. This documentation can be your best defense.
- Separate decision-making: If you’re in the middle of handling a compliance complaint, let someone outside the situation—like your compliance officer or HR—review any proposed actions against the employee.
- Follow established protocols: Deviating from your normal policies, especially when dealing with someone who has raised a complaint, can make it look like you are targeting them.
- Train your leaders: Everyone in management needs to understand what retaliation looks like and how to avoid it.
Leadership sometimes expresses concerns about employees “stirring up trouble” or raising issues for self-protection. But the law doesn’t distinguish between “valid” and “troublesome” complaints. Protected activity is protected activity, full stop.
Take a step back. If you’re ever considering taking action against an employee who has engaged in protected activity, discuss it first with your HR or compliance team. Together, you can ensure the decision is based on legitimate, well-documented reasons and not influenced—even unconsciously—by the complaint itself.
At the end of the day, your goal is to serve patients and families with integrity and compassion. That means creating a culture where employees feel safe to speak up about compliance issues without fear of retaliation. Protecting that culture isn’t just about avoiding lawsuits—it’s about doing what’s right for your team, your agency, and the people you care for.

by editor | Oct 13, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, Interdisciplinary Team, Regulatory Compliance, Rules and Regulations - Chaplains, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers
The hospice interdisciplinary group (IDG) creates a patient’s plan of care and provides holistic care to the patient, caregiver, and family. Hospice Conditions of Participation require the IDG to “review, revise, and document the individualized plan as frequent as the patient’s condition requires, but no less frequently than every 15 calendar days.”
As such, the IDG meet at a minimum every 15 days. In many hospice organizations, the interdisciplinary group meets weekly to review patient status and to determine if changes are required to a patient’s plan of care. It is important that during the IDG meeting patients’ care plans are reviewed and updated based upon patients’ assessments. Timely and accurate documentation is critical; this documentation may be reviewed by surveyors and by CMS to ensure compliance with regulations.
Who is required to attend an IDG Meeting
Required members of the IDG meeting include:
- A doctor who is an employee or under contract with the hospice agency
- Registered nurse
- Social worker
- Pastoral or other counselor
These four individuals are minimum participants in the IDG meeting. If one of these members i missing from the IDG meeting, the meeting does not meet Medicare regulations and it is considered as if the meeting did not take place. . Care must be taken to ensure that the minimum requirement – IDG meeting with the participation of at least these four individuals at a minimum of once every 15 days – is met.
Additionally, a staff member is typically identified to serve as the scribe for the IDG meeting. The scribe captures any changes to a patient’s plan of care that are agreed upon during the meeting.
What activities occur during the IDG meeting?
When the meeting begins, all participants sign the meeting sign-in sheet. These sheets serve as documented proof that the hospice has met the Medicare Conditions of Participation – that the required members of IDG participated in the meeting. Sign in sheets are stored in a place that is accessible for review upon the request of auditors or surveyors.
Prior to the IDG meeting, a list is drawn up of the patients who will be reviewed during the meeting. For each of these patient’s members of the care team provide an update on the patient’s current condition, highlighting any concerns. The team then discusses the plan for the upcoming two weeks.
Patients may be ordered for discussion as follows:
- Deaths
- Admissions
- Recertifications
- Evaluation
Let’s review each of these in detail.
Deaths
Each death since the prior IDG meeting is reviewed. The team discusses whether bereavement has been requested or declined. In the case where bereavement has been requested, the individuals who will be receiving bereavement services are identified. Any further details or concerns on the services that will be provided are discussed.
Admissions
The RN Case manager discusses any new admissions since the prior IDG meeting, including patient diagnosis and hospice eligibility criteria. Visit frequency is discussed, hospice aide services, and patient psychosocial needs. Typically, all team members partake in this discussion including a discussion about patient medications and prognostic indicators.
Recertifications
At this stage in the IDG the team discusses all patients who are the end of their benefit period and need to be recertified. Any face-to-face visits that were conducted will be discussed and any that are still pending will need to be scheduled. For patients who were evaluated and are found not to meet criteria, the team discusses how to notify the family and details on how to transition the patient off of hospice care.
Evaluations
All remaining patients on the list are reviewed by the members of the IDG. The team discusses whether any changes to the plan of care are needed, whether any medications need to be changed or if any additional support is required (e.g., chaplain, volunteer). The plan of care may be updated if the team agrees that a change in visit frequency is required.
Updating patients’ plan of care
While each patient is discussed, any changes to the patient’s plan of care are entered into the patient’s chart, which is signed by the medical director.
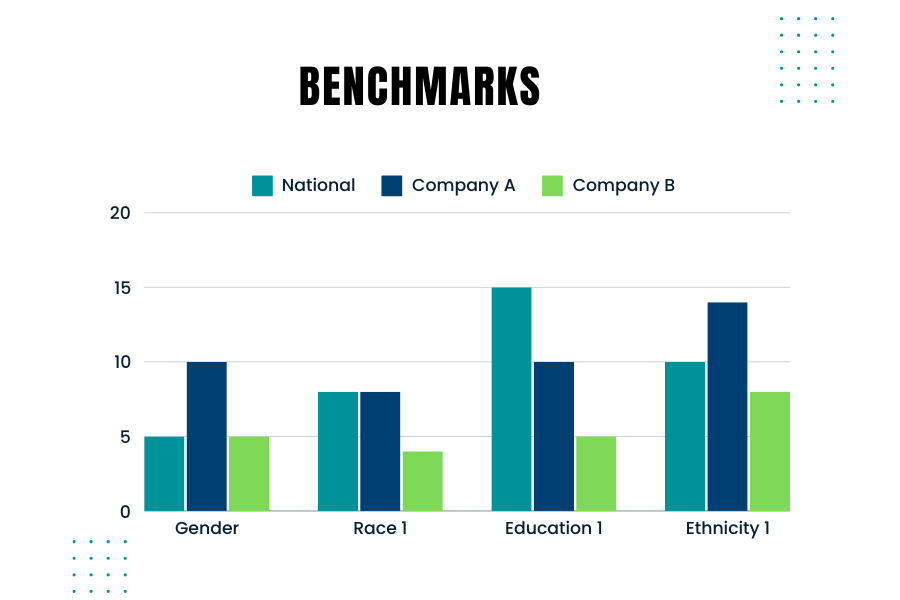
by editor | Aug 3, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Human Resources, Regulatory Compliance
Creating and using benchmarks to compare your company’s hiring demographics against those used by government agencies like the EEOC (Equal Employment Opportunity Commission) is crucial. Benchmarking helps ensure that your company’s hiring practices are fair and compliant with federal regulations. Here’s are some considerations to keep in mind when you consider the right benchmarks
Why Benchmarking Matters
Government agencies monitor and require companies to report on the demographic composition of their workforce, especially larger companies. For instance, the EEOC uses benchmarks to compare a company’s demographics against broader population data from sources like the U.S. Census and the American Community Survey. Knowing how your company’s demographics stack up against these benchmarks is essential for several reasons:
- Compliance: Ensuring your hiring practices comply with laws such as the Civil Rights Act and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act.
- Diversity Goals: Meeting your company’s diversity and inclusion goals.
- Fair Hiring Practices: Ensuring fair and unbiased hiring practices.
Best Practices for Benchmarking
- Collect Internal Data: Gather detailed demographic data of your current workforce and applicants.
- Ensure you track data on race, gender, age, and other relevant demographics.
- Choose the Right External Data: Depending on your hiring scope, use national, regional, or local data. For example, if you recruit nationwide, use national benchmarks. For local hires, consider regional data.
- Occupation and Industry-Specific Data: Align your benchmarks with the specific occupations and industries relevant to your company. Different industries and roles may have distinct demographic compositions.
- Adjust for Educational Requirements: Consider the educational requirements for the roles you are hiring. This will help you compare your applicant pool against the qualified population.
- Use Census Data: The U.S. Census Bureau provides comprehensive data that can be segmented by occupation, geography, and other factors. This data is a good starting point for creating your benchmarks.
Ensuring Fair Selection
To avoid over- or under-selecting any protected group, follow these steps:
- Regularly Update Benchmarks: Demographic data changes over time. Ensure your benchmarks are based on the most recent data.
- Monitor Hiring Practices: Continuously monitor your hiring practices and outcomes against your benchmarks.
- Training and Awareness: Educate hiring managers on the importance of diversity and compliance with hiring practices.
External Data Sources
Looking at external data sources is important because it provides a broader context for your internal data. It helps you understand the labor market and demographic trends in your industry and location. External benchmarks serve as a snapshot of the current workforce composition, which can change over time.
Creating effective benchmarks involves a blend of using accurate external data and understanding your company’s unique needs. By comparing your company’s demographics against reliable benchmarks, you can ensure fair and compliant hiring practices. Regularly updating these benchmarks and educating your hiring team on best practices will help maintain a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Where Can You Find Additional Information?
- Of Significance: Don’t Miss the Mark! Podcast on what to keep in mind when creating benchmarks
- Harvard Business Review: Smart benchmarking starts with knowing whom to compare yourself to

by editor | Feb 14, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Regulatory Compliance
The hospice Special Focus Program (SFP) is conducted by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The objective of this program is to identify poor performing hospice agencies, based upon quality indicators, that place hospice beneficiaries at risk. These hospice agencies will then be subject to additional scrutiny and oversight to ensure that they meet Medicare requirements. The SFP is designed to either bring these programs into compliance or force them out of the Medicare program by terminating their Medicare status.
What is the origin of the Special Focus Program?
The hospice Special Focus Program was mandated in the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021. That is also when it was clarified that hospices would be surveyed every three years. All hospices now have had a survey since 2021. Some of that data is being used for the hospice Special Focus Program, which is designed to identify the worst performing hospices and either bring them into compliance or force them out of the program by terminating their Medicare status.
How is a hospice agency selected for inclusion in the Special Focus Program?
CMS uses an algorithm to identify the poor performing hospice agencies to include in the SFP. The algorithm combines data from a few data sources to score each of the hospice agencies. The score is based on data from: condition-level deficiencies in standard surveys, substantiated complaints, Hospice Care Index (HCI), and the CAHPS survey. The algorithm does not stratify hospice agency based upon size or location; all hospice agencies are held to the same standard regardless of their size or location. The bottom 10% ranked hospice agencies (which are the hospice agencies with the highest algorithm score) are selected to be included in to the SFP.
What is the impact of a hospice agency being included in the SFP?
Hospice agencies that are included in the SFP will be publicly reported on the SFP website. SFP is a framework for increased oversight. The hospice agencies that are included in the SFP program will be surveyed more frequently — at least every six months. CMS will determine what actions must be taken based upon the survey results.
How will a hospice agency exit the SFP?
A hospice will complete the SFP if in an 18-month time frame the hospice agency has no Quality of Care condition level deficiencies or immediate jeopardies for any two six month SFP surveys and has no pending complaints or have returned to substantial compliance with all requirements. The hospice will receive a letter from CMS that will indicate official completion of the program. If a hospice is unable to meet the completion criteria – due to inability to successfully pass surveys or continued complaints while on the SFP – it will be placed on the Medicare termination track.
Even as hospices work to improve their levels of quality and compliance, there will always be hospice agencies that fall in the lowest 10% of performance relative to their peers. Only by continually monitoring their quality performance and comparing these quality scores to peer performance can a hospice agency stay out of the lower 10% and off of the SFP list.
Where can you find out more?
Hospice Special Focus Program – CMS

by editor | Jan 29, 2023 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, QAPI, Regulatory Compliance
What is the governing body?
In accordance with the Conditions of Participation, a Medicare certified hospice agency must have a governing body. The governing body has ultimate responsibility for the hospice agency, including legal and financial authority. Medicare Conditions of Participation require that the governing body is informed of the ongoing activities at the hospice agency, including patient care delivery issues and all QAPI activities. The governing body must also appoint a qualified hospice administrator – a hospice employee with the necessary education and experience – who is responsible for hospice daily operations.
The governing body must meet at least quarterly and must maintain written minutes of its meetings.
There are two Conditions of Participation – 418.100 and 418.58 – that relate to the hospice governing body.
Condition of Participation 418.100
This Condition of Participation defines a standard that the governing body is responsible for management of the hospice agency, including its fiscal operations, provision of services, and continuous quality assessment and performance improvement (QAPI) efforts. The governing body also assumes full legal authority of all hospice operations. It further specifies that the governing body should appoint an administrator that reports to the governing body and who is responsible for hospice agency daily operations. The hospice administrator must be a hospice employee and must have necessary training, education, and experience. CMS does not specify the process by which an administrator should be selected by the governing body. If a hospice agency has multiple locations, the governing body is responsible for administration, supervision, and services for all locations as well as for any arranged services.
Condition of Participation 418.58
This Condition of Participation discusses requirements of a hospice agency’s QAPI program. The governing body must ensure that the hospice agency maintains and implements an ongoing quality improvement and patient safety program. Program performance must be monitored on a regular basis. Further, the governing body must ensure that one or more individuals are selected to lead the organization’s QAPI efforts.
The hospice agency’s organization documents must specify that the hospice governing body is responsible for the QAPI program. Additionally, the governing body specifies the frequency of data collection and level of detail of data collected by the QAPI program.
Are there any state regulations?
State hospice licensure regulations may impose additional requirements on the hospice governing body. They may also have specific requirements on the administrator that is selected by the governing body. A hospice is required to meet the most stringent requirements (whether state or federal).
Surveyors will check that all conditions are met. A hospice agency should maintain evidence of the governing body’s role and activities. Governing body authorizations and activities should be documented in governing body meeting minutes, company organization documents, and company policies and procedures.
Where can you find out more?
CMS Conditions of Participation – Governing Body





