
by editor | Aug 25, 2024 | Care Keys - Aides, Care Keys - Chaplains, Care Keys - Nurses, Care Keys - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Office Team, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Volunteers
As a member of the hospice healthcare team, you play an important role in caring for your patients. Because of this, you will often learn private information about them – not just about their health, but also about their personal relationships, their financial situations, and other sensitive and personal information. It is important to understand that you have a legal and ethical responsibility to keep this information confidential and only share it – when necessary – with other healthcare professionals who are part of the patient’s care team. It is your responsibility to protect patient privacy.
Why is it important to keep healthcare information private?
In 1996, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was passed to protect people’s health information. The main goal of HIPAA is to ensure that health information is kept private and secure, and only shared with those who need to know in order to provide care or process medical records. This law applies to everyone working in healthcare.
What does HIPAA protect?
HIPAA protects what is called “personal health information” (PHI). This includes any details that could identify a patient, such as:
- Name
- Medical record number
- Date of birth
- Address
- Email address
- Social security number
Only those directly involved in a patient’s care or those who handle billing or administrative tasks should have access to this information.
Your role as a member of the patient’s healthcare team
As a member of the patient’s healthcare team, it is important to follow HIPAA rules to protect your patient’s privacy. If you share a patient’s health information without permission, it can harm the patient and break the trust they have in you. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
- Do not share information unnecessarily: Never discuss a patient’s health with friends, family, or on social media. Only discuss patient care with other healthcare workers who are directly involved in that patient’s care.
- Keep conversations private: If you need to talk about a patient’s care with another healthcare worker, make sure you do so in a private place where others cannot overhear.
- Secure patient records: Whether you are handling paper records or using electronic systems, always ensure that patient information is stored securely.
Why following HIPAA is important
By following HIPAA regulations, you help protect your patient’s privacy, ensure their information is handled with respect, and build trust. Patients and their families rely on you to keep their personal information safe, and HIPAA provides the guidelines you need to do so.
What are the guidelines of not following HIPAA?
Hospices and their employees must protect patient information at all times. If HIPAA rules are not followed, it can lead to serious consequences including fines, penalties, and even imprisonment. This applies not just to the hospice itself but also to any vendors or contractors who work with patient information.
Final thoughts
Understanding and following HIPAA is an essential part of your job as a member of a patient’s healthcare team. By keeping patient information private, you help ensure their safety, comfort, and trust in the care they receive. Remember, protecting privacy is not just a legal requirement – it is a crucial part of providing compassionate and respectful care.
Where can you find more information
by editor | Dec 11, 2022 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Documentation - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, Medical Records, Patient Care, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Volunteers
What is the purpose of hospice quality reporting?
The Affordable Care Act authorized the establishment of a Quality Reporting Program for hospices. The Hospice Quality Reporting Program (HQRP) was established in 2014. HQRP aims to ensure that the level of quality in clinical care, symptom management, and patient and family experiences is at a high level across all hospice agencies. HQRP further aims to help patients and their families make informed decisions about end-of-life care. The measures and benchmarks reported in HQRP also provide CMS with measurements of hospice agency performance and how agencies are performing relative to other agencies in their region and across the nation. Some of the measures can also be used as indicators of Medicare fraud or abuse.
The Affordable Care Act also requires that quality measures relating to hospice care are reported on a CMS website.
HQRP data collection began in 2014 with two components. The first component was related to Hospice Item Set (HIS) data collection and transmission. The second component was related to the Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS) Hospice Survey participation.
The Hospice Compare website was launched in 2017, enabling patients and their families to compare between the performance of different hospice agencies. In December 2020, Hospice Compare was replaced by Care Compare.
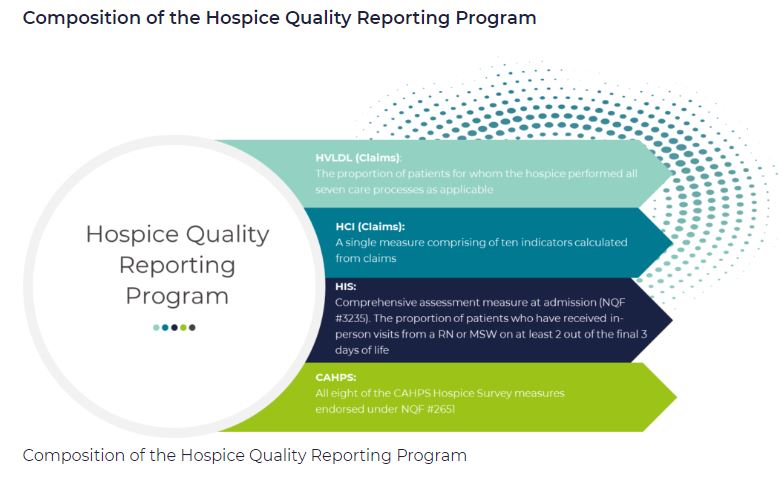
Which measures are included in HQRP?
HQRP measures care across a patient’s hospice stay. With a commitment to quality improvement, data transparency, and informed decision-making, the number of HQRP measures has increased since the launch of the program. As of 2022, HQRP includes four metrics, each of which includes several underlying measures:
What determines HQRP Compliance?
Performance level is not considered when determining compliance with HQRP; CMS requires a hospice agency to submit data completely, and on time, to be considered compliant. A Medicare-certified hospice agency is HQRP compliant if it submits the required data within the required timeframe and the data is accepted. A hospice agency is not compliant if it submits data but the data is not accepted. Failure to comply with HQRP requirements results in a two percentage point reduction in Annual Payment Update (APU). That is, for a hospice agency to preserve its full payment update, the agency must meet all HQRP data submission requirements. Failure to submit results will also impact an agency’s results on Care Compare.
How does CMS use the data that is submitted?
CMS currently uses the collected data internally for strategic planning purposes. CMS also uses the act of reporting to raise attention and awareness and promote actions to improve patient care.
Can a hospice agency verify its HQRP data before it is publicly published?
A hospice agency can review its HQRP data via the CASPER system before the results are made public on Care Compare. CASPER reports can be accessed by selecting the CASPER Reporting link to the CMS Quality Improvement and Evaluation System (QIES) Systems for Providers webpage. Hospice-specific reports are located in the Hospice Provider and Hospice Quality Reporting Program reporting categories in CASPER. Hospice agencies should review this data before it is published on Care Compare to ensure data accuracy, since the published data is used by the public to compare and select a hospice agency for end-of-life care.
Where can you find more information?
by editor | Sep 15, 2022 | Accounts Payable, Billing, Billing - General, Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Documentation - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, Human Resources, Intake, Medical Records, Metrics and KPIs, Office Setup, Payroll, Rules and Regulations - Chaplains, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Volunteers
Are you confused by the Acronym Alphabet Soup?
Does the never ending list of acronyms used in the hospice and healthcare industry leave you confused?
Are you worried that you may confuse CMN with CMP?
To help sort out the confusion, we add here links to lists of acronyms:
Use these acronym listings to help clarify things when you inevitably are faced with acronym confusion!




