
by editor | Oct 13, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, Interdisciplinary Team, Regulatory Compliance, Rules and Regulations - Chaplains, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers
The hospice interdisciplinary group (IDG) creates a patient’s plan of care and provides holistic care to the patient, caregiver, and family. Hospice Conditions of Participation require the IDG to “review, revise, and document the individualized plan as frequent as the patient’s condition requires, but no less frequently than every 15 calendar days.”
As such, the IDG meet at a minimum every 15 days. In many hospice organizations, the interdisciplinary group meets weekly to review patient status and to determine if changes are required to a patient’s plan of care. It is important that during the IDG meeting patients’ care plans are reviewed and updated based upon patients’ assessments. Timely and accurate documentation is critical; this documentation may be reviewed by surveyors and by CMS to ensure compliance with regulations.
Who is required to attend an IDG Meeting
Required members of the IDG meeting include:
- A doctor who is an employee or under contract with the hospice agency
- Registered nurse
- Social worker
- Pastoral or other counselor
These four individuals are minimum participants in the IDG meeting. If one of these members i missing from the IDG meeting, the meeting does not meet Medicare regulations and it is considered as if the meeting did not take place. . Care must be taken to ensure that the minimum requirement – IDG meeting with the participation of at least these four individuals at a minimum of once every 15 days – is met.
Additionally, a staff member is typically identified to serve as the scribe for the IDG meeting. The scribe captures any changes to a patient’s plan of care that are agreed upon during the meeting.
What activities occur during the IDG meeting?
When the meeting begins, all participants sign the meeting sign-in sheet. These sheets serve as documented proof that the hospice has met the Medicare Conditions of Participation – that the required members of IDG participated in the meeting. Sign in sheets are stored in a place that is accessible for review upon the request of auditors or surveyors.
Prior to the IDG meeting, a list is drawn up of the patients who will be reviewed during the meeting. For each of these patient’s members of the care team provide an update on the patient’s current condition, highlighting any concerns. The team then discusses the plan for the upcoming two weeks.
Patients may be ordered for discussion as follows:
- Deaths
- Admissions
- Recertifications
- Evaluation
Let’s review each of these in detail.
Deaths
Each death since the prior IDG meeting is reviewed. The team discusses whether bereavement has been requested or declined. In the case where bereavement has been requested, the individuals who will be receiving bereavement services are identified. Any further details or concerns on the services that will be provided are discussed.
Admissions
The RN Case manager discusses any new admissions since the prior IDG meeting, including patient diagnosis and hospice eligibility criteria. Visit frequency is discussed, hospice aide services, and patient psychosocial needs. Typically, all team members partake in this discussion including a discussion about patient medications and prognostic indicators.
Recertifications
At this stage in the IDG the team discusses all patients who are the end of their benefit period and need to be recertified. Any face-to-face visits that were conducted will be discussed and any that are still pending will need to be scheduled. For patients who were evaluated and are found not to meet criteria, the team discusses how to notify the family and details on how to transition the patient off of hospice care.
Evaluations
All remaining patients on the list are reviewed by the members of the IDG. The team discusses whether any changes to the plan of care are needed, whether any medications need to be changed or if any additional support is required (e.g., chaplain, volunteer). The plan of care may be updated if the team agrees that a change in visit frequency is required.
Updating patients’ plan of care
While each patient is discussed, any changes to the patient’s plan of care are entered into the patient’s chart, which is signed by the medical director.

by editor | Oct 7, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Hospice 101 - Aides, Hospice 101 - Chaplain, Hospice 101 - Nurses, Hospice 101 - Office Team, Hospice 101 - Social Workers, Interdisciplinary Team
Hospice care is patient- and family-centered, where the patient’s and family’s preferences and needs drive the care plan.
The hospice interdisciplinary group (also referred to as Hospice IDG or IDG), also referred to as the interdisciplinary team (IDT) is a team of healthcare professionals who work together to create a plan tailored to the needs of hospice patients. The IDG is crucial because it reflects the fundamental principle of hospice care: a multidisciplinary and holistic approach to treating a patient. Hospice care is not just about managing medical symptoms; it involves addressing the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs of the patient and their family. This comprehensive care model requires combined expertise of different healthcare professionals working together as a cohesive team.
Multidisciplinary and 360-degree approach
The idea of a multidisciplinary approach is central to hospice care because a single healthcare professional cannot fully address the complex needs of a patient at the end of life. Hospice patients often experience pain, emotional distress, social isolation, and spiritual concerns, all of which need to be treated so that the patient has a peaceful and dignified end of life experience. Each of the members of the IDG can address different aspects of hospice patient needs.
Physical needs: Managed by the physician and nurse. The physician provides medical direction and oversees patient care while the nurse manages the patient’s medical needs such as pain control and symptom management.
Emotional and social needs: The social worker provides emotional and social support, caring for emotional health, caregiver stress, and family dynamics. Consideration is also given to connecting the family with community resources
Spiritual needs: These are managed by the chaplain, who offers spiritual care and counseling, based on the patient’s and family’s beliefs. The chaplain helps patients and families explore spiritual concerns, questions of meaning, or religious beliefs in the context of their journey.
Daily living needs: Hospice aides assist with personal care like bathing, dressing, and grooming. They ensure dignity and comfort in activities of daily living like bathing, dressing, and grooming.
Companionship and support: The hospice volunteer offers companionship and practical help, like errands or respite for family caregivers.
By involving individuals from different disciplines, hospice care can take a 360-degress approach to a patient’s needs. It means that every aspect of care – physical, emotional, social, and spiritual – is addressed by someone with the expertise to manage that particular dimension. This all encompassing approach is what makes hospice care unique and effective.
Are all member of the IDG required per CMS regulations?
Per CMS regulations, only core members must always be part of the IDG to ensure that hospice care addresses every critical aspect of the patient’s experience. Four disciplines are considered core required members of the team. These include:
- Physician
- Registered nurse
- Social worker
- Chaplain
Some professional members may be included in the IDG as needed, depending upon patient’s individual circumstances. These include:
- Hospice Aide
- Volunteer
- Therapists
- Bereavement Counselor
How is the IDG aligned with regulatory standards?
CMS requires that hospice care involve an interdisciplinary approach because it reflects the need to treat the “whole” patient, not just their medical condition. The IDG ensures that the care plan is tailored to the patient’s evolving needs and that it incorporates feedback from multiple disciplines to achieve the best outcomes. The interdisciplinary model is also a regulatory requirement under the hospice Conditions of Participation (CoPs). As such, surveyors will review the functioning of the IDG during inspections to ensure compliance. A well coordinated interdisciplinary team ensures regulatory compliance and quality patient care.
Why is the interdisciplinary hospice team essential?
Hospice care is patient and family centered, meaning that the patient’s and family’s preferences and needs drive the care plan. The IDG works collaboratively to ensure that the care plan remains flexible and responsive to changes in the patient’s condition. As hospice patients often experience rapid changes in health, having professionals from different disciplines ensures that all aspects of care can be addressed promptly and effectively.
In summary, the IDG reflects hospice’s holistic, multidisciplinary approach to care by ensuring that all dimensions of the patient’s well-being are addressed. Required team members focus on medical, emotional, and spiritual care, while optional members can be added to meet unique or additional needs. This alignment ensures that hospice remains flexible and patient-centered.

by editor | Aug 25, 2024 | Care Keys - Aides, Care Keys - Chaplains, Care Keys - Nurses, Care Keys - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Office Team, Rules and Regulations - Social Workers, Rules and Regulations - Volunteers
As a member of the hospice healthcare team, you play an important role in caring for your patients. Because of this, you will often learn private information about them – not just about their health, but also about their personal relationships, their financial situations, and other sensitive and personal information. It is important to understand that you have a legal and ethical responsibility to keep this information confidential and only share it – when necessary – with other healthcare professionals who are part of the patient’s care team. It is your responsibility to protect patient privacy.
Why is it important to keep healthcare information private?
In 1996, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was passed to protect people’s health information. The main goal of HIPAA is to ensure that health information is kept private and secure, and only shared with those who need to know in order to provide care or process medical records. This law applies to everyone working in healthcare.
What does HIPAA protect?
HIPAA protects what is called “personal health information” (PHI). This includes any details that could identify a patient, such as:
- Name
- Medical record number
- Date of birth
- Address
- Email address
- Social security number
Only those directly involved in a patient’s care or those who handle billing or administrative tasks should have access to this information.
Your role as a member of the patient’s healthcare team
As a member of the patient’s healthcare team, it is important to follow HIPAA rules to protect your patient’s privacy. If you share a patient’s health information without permission, it can harm the patient and break the trust they have in you. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
- Do not share information unnecessarily: Never discuss a patient’s health with friends, family, or on social media. Only discuss patient care with other healthcare workers who are directly involved in that patient’s care.
- Keep conversations private: If you need to talk about a patient’s care with another healthcare worker, make sure you do so in a private place where others cannot overhear.
- Secure patient records: Whether you are handling paper records or using electronic systems, always ensure that patient information is stored securely.
Why following HIPAA is important
By following HIPAA regulations, you help protect your patient’s privacy, ensure their information is handled with respect, and build trust. Patients and their families rely on you to keep their personal information safe, and HIPAA provides the guidelines you need to do so.
What are the guidelines of not following HIPAA?
Hospices and their employees must protect patient information at all times. If HIPAA rules are not followed, it can lead to serious consequences including fines, penalties, and even imprisonment. This applies not just to the hospice itself but also to any vendors or contractors who work with patient information.
Final thoughts
Understanding and following HIPAA is an essential part of your job as a member of a patient’s healthcare team. By keeping patient information private, you help ensure their safety, comfort, and trust in the care they receive. Remember, protecting privacy is not just a legal requirement – it is a crucial part of providing compassionate and respectful care.
Where can you find more information

by editor | Aug 14, 2024 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Human Resources, Payroll
As a manager in hospice care, your role goes beyond overseeing patient care and managing staff. It includes ensuring that your team feels valued and fairly compensated. Pay transparency is becoming a hot topic, and understanding its implications can help you effectively navigate this evolving landscape.
What Is Pay Transparency?
Pay transparency refers to the practice of openly sharing information about compensation within an organization. This can include posting salary ranges in job listings, discussing pay openly among employees, or providing detailed breakdowns of how pay is determined. The goal is to ensure that employees understand how their pay is calculated and that there are no disparities based on gender, race, or other factors.
What is the status of pay transparency regulations in the U.S.?
The U.S. is starting to experience a trend in adoption of pay transparency regulations. Several states have introduced laws that require employers to provide salary ranges in job postings or upon request. For example:
- Colorado: The state’s Equal Pay for Equal Work Act requires employers to include salary ranges in job postings and provide pay information to employees upon request.
- New York City: The city requires employers with four or more employees to include salary ranges in job advertisements.
- California: As of January 2023, California employers with 15 or more employees must include pay scales in job postings.
It is likely that more states will follow and that the laws with transparency requirements will continue to be more comprehensive.
Why Is Pay Transparency Important?
- Fosters Trust and Engagement: When employees understand how their pay is determined and believe it is fair, they are more likely to feel valued and engaged in their work. In a field as emotionally demanding as hospice care, high employee engagement is crucial for maintaining a positive work environment and delivering high-quality care.
- Reduces Pay Disparities: Pay transparency helps to identify and address pay disparities that may exist within your organization. In healthcare, where women and minorities are often overrepresented in lower-paying roles, transparency can be a tool for promoting equity and ensuring that all employees are paid fairly for their work.
- Compliance with Regulations: Some states in the U.S. are implementing laws that require employers to provide pay ranges in job postings or share salary information upon request. Staying ahead of these regulations by adopting pay transparency practices can help your hospice avoid legal challenges and demonstrate a commitment to fairness.
How to Implement Pay Transparency
- Review Current Pay Practices: Start by conducting a thorough review of your current pay practices. Ensure that salaries are consistent with market rates and that there are no unexplained disparities among employees with similar roles and experience levels.
- Communicate Clearly: If you decide to move towards more transparency, communicate clearly with your team about what information will be shared and why. For example, explain how pay ranges are determined and what factors influence individual salaries.
- Train Managers: Provide training for all managers to ensure they understand the principles of pay transparency and are equipped to have open and honest conversations about pay with their team members.
- Update Job Postings: If your state requires it or if you choose to do so, include salary ranges in job postings. This not only meets regulatory requirements but also attracts candidates who appreciate transparency and fairness.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Pay transparency is not a one-time effort. Regularly review your compensation practices and make adjustments as needed to ensure ongoing fairness and compliance with any new laws or guidelines.
Challenges of Pay Transparency
- Managing Expectations: One of the challenges of pay transparency is managing employee expectations. If employees see that their pay is lower than a colleague’s, they may feel undervalued, even if there are legitimate reasons for the difference. It’s important to be prepared to explain these differences clearly and fairly.
- Confidentiality Concerns: In some cases, employees may prefer to keep their salaries private. It’s important to balance transparency with respect for individual preferences and privacy.
- Complexity in Pay Structures: Healthcare organizations often have complex pay structures with various factors influencing salaries, such as certifications, years of experience, and additional responsibilities. Transparency requires clear communication about these complexities, which can be challenging.
The Future of Pay Transparency in the U.S.
It is likely that the U.S. will continue to see increased pressure for transparency in the coming years. The healthcare industry, including hospice care, may need to adapt to more stringent regulations and expectations around pay disclosure.
As a manager, staying informed about these trends and proactively implementing transparent pay practices can position your hospice to lead in this area. Not only will this help in complying with potential future regulations, but it will also foster a more equitable and supportive work environment for your team.
Conclusion
Pay transparency is an important and evolving issue. Adopting transparent pay practices now can help foster trust, promote fairness, and ensure compliance with current and future regulations. By being proactive in this area, you can create a more equitable and positive work environment for your team, ultimately leading to better care for your patients.
Where Can You Find Out More
- Gallagher: How managers can respond to pay transparency
- SHRM: How Companies can Respond to New Pay Transparency Laws
- Payscale: How to implement pay transparency
- World at Work: Pay Transparency – Risk, Rewards, and Regulations
- Harvard Business Review: Complicated Effects of Pay Transparency
by editor | Mar 22, 2023 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Metrics and KPIs, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Office Team
Patient length of stay is monitored to detect instances of inappropriate use of the hospice benefit or other deficiencies in the services delivered by the hospice provider. Length of stay is monitored for both very short length of stay as well as for length of stay that is longer than the norm.
What may unusual length of stay tell a hospice provider?
When patients are discharged alive with a short length of stay it may signal that the patient did not understand the hospice benefit when the patient was admitted to hospice. Or, patients may discharge live from hospice after just a few days because they were not satisfied with the services delivered by the hospice provider. Patients with length of stay longer than 180 days could be indicative of a patient who is no longer hospice eligible. Patients who are no longer eligible for service should be discharged from hospice and any payments that were received from Medicare while the patient was no longer eligible for services should be returned to Medicare. Failure to discharge the patient or failure to return the funds are examples of fraud and abuse.
How is length of stay calculated?
Length of stay is calculated based on the number of days that a patient receives hospice care. Specifically, for a patient who is discharged from hospice (whether or not the patient is discharged alive), the patient length of stay is calculated as follows:
Patient length of stay = [patient discharge date]-[patient admission date]+1
Which patients are included in length of stay calculation?
The length of stay calculation assumes that only discharged patients are considered in the calculation – since the formula expressly refers to the patient discharge date. When only discharged patients are considered (whether live discharges or discharges due to death), the hospice provider only has a backward-looking view on performance relating to length of stay. For example, if a hospice provider has been providing service to a patient for 12 months and the patient is still on service, the patient will not be included in the traditional average length of stay metric – since the patient has not yet been discharged. On the other hand, once the patient is discharged the patient’s length of stay will be at least 365 days since the patient – while still currently active – has already been on service for 365 days. If active patients are considered in a length of stay calculation, it gives a hospice provider a metric that can be used to highlight patients whose clinical charts and documentation of care may benefit from additional review.
What length of stay metrics should be calculated?
In addition to computing average and median length of stay based on discharged patients only, average and median length of stay can be computed for active patients. Patient length of stay for an active patient is calculated as follows:
Active patient length of stay = [end of evaluation period date]-[patient admission date]+1
For example, suppose the current date March 15, 2023 and a hospice wishes to calculate the active patient length of stay as of the end of 4Q 2022 for a patient who was admitted on December 1, 2022. The calculation is as follows:
- End of evaluation period date: 12/31/22
- Patient admission date: 12/1/22
- Active patient length of stay = (12/31/22) – (12/1/22) + 1 = 31 days
The active patient length of stay as of the end of 4Q 2022 is 31 days.
If the hospice wishes to calculate the active patient length of stay as of current date, the calculation is as follows:
- End of evaluation period date: 3/15/23
- Patient admission date: 12/1/22
- Active patient length of stay = (3/15/23) – (12/1/22) + 1 = 105 days
Average and median length of stay would be computed as usual. If any concerning value — such as long length of stay – is identified based upon the active patient length of stay, a hospice provider can immediately investigate and determine if any remediation action is required, rather than waiting until patients are discharged. Delay can lead to additional fines or further action from Medicare.
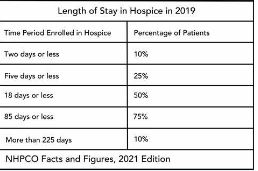
by editor | Mar 22, 2023 | Compliance and Regulatory - Directors, Metrics and KPIs, Rules and Regulations - Nurses, Rules and Regulations - Office Team
Patients are eligible for hospice if they have a terminal diagnosis and a prognosis of six or fewer months to live if their disease runs its natural course. A patient who lives longer than six months can still get hospice care if the medical director or other hospice physician recertifies that the patient is still terminally ill.
What is hospice patient length of stay?
Hospice length of stay is an important metric that is monitored by both CMS and by hospice providers. Hospice length of stay measures the count of days that a patient receives hospice services, from the day that the patient is admitted into hospice until the day the patient is discharged (either alive or deceased). In 2018, 25% of Medicare beneficiaries received hospice care for seven days or less and 54% of Medicare beneficiaries received hospice care for 30 days or less.
Why should a hospice monitor patient length of stay?
Monitoring patient length of stay can aid in detecting cases of possible fraud or abuse – instances where ineligible patients continue to receive the hospice benefit. This metric also helps monitor whether the hospice benefit is being adequately utilized. Although patients are eligible for hospice when they have six months or less to live, most patients receive less than 30 days of hospice care.
Agency patient length of stay is also trended over time and is also compared against the value for patients in the same region, state, or nationwide. The metric may also be analyzed for patients in subpopulations – for example patients with the same disease, race, or ethnicity.
How is patient length of stay calculated?
Patient length of stay is calculated using all patients discharged by the hospice provider during the reporting period. For example, if the hospice would like to compute the length of stay for patients during the 4Q 2022, all patients who were discharged during 1Q 2023 would be included in the calculation. For each patient, the number of days from the date of patient admission until the date of patient discharge is counted; this represents the patient length of stay.
Patient length of stay = [patient discharge date]-[patient admission date]+1
What are common measures of length of stay?
Two common patient hospice length of stay measures are Average Length of Stay (ALOS) and Median Length of Stay (MLOS).
Average length of stay
Average length of stay is the arithmetic mean of the data collected. Specifically, if d is patient length of stay and N is the total number of patients then average length of stay (ALOS) is calculated as follows:
ALOS = ( d1 + d2 + d3 + …. + dn ) /N
Where di = patient length of stay for patient i
Median length of stay
Median length of stay is the middle number in the sequence of numbers. Specifically, compute the length of stay for all N patients. Then, order these N numbers in ascending order. The middle number is the median. If the number of patients is even then there is no middle number. Instead, the median is calculated by taking the average of the two numbers in the middle.
Comparing average and median length of stay
The average is sensitive to outliers in the data. That is, if there are a few patients with a very high length of stay while all other patients have a significantly lower length of stay, the average will be biased by these outliers and will give a misleading assessment of overall patient length of stay. Below, we give an example to provide greater intuition into the impact of outliers on average length of stay and the difference between mean and median length of stay.
Suppose a hospice agency discharged 35 patients during 4Q 2022. The patients’ lengths of stay are as follows:

We compute the average length of stay by summing each of the 35 patient’s length of stay (in the “Length of Stay” column) and dividing that total by 35 (the total count of patients).
Average length of stay (ALOS) = 38.5
We compute the median length of stay by sorting the patient’s length of stay in ascending order and identifying the central number. Since there is an odd number of patients, there will be a single central value. In this case, the central value is 20.
Median length of stay (MLOS) = 20
Average length of stay is almost double the median length of stay. What is leading to these significant differences between ALOS and MLOS? Observe the outliers in the data. There are two patients with length of stay that exceeds 200 days. There are two additional patients with length of stay exceeding 100 days. Since ALOS is sensitive to outliers, ALOS is being pulled to a higher value due to the presence of these outliers.
To provide additional insight, we have plotted a histogram of the length of stay values. A histogram shows the count of observations in the data that fall in each of the specified ranges.

The table on the left shows the count (frequency) of observations of patient length of stay in the data for each of the ranges: 0-10 days, 10-20 days, 20-30 days, 30-40 days, and greater than 40 days. There are 11 patients with length of stay between 0-10 days, 7 patients with length of stay between 10-20 days, 6 patients with length of stay between 20-30 days, 6 patients with length of stay between 30-40 days, and 4 patients with length of stay that exceeds 40 days.
Think about this histogram and now consider the MLOS and ALOS. Median length of stay is 20 days – it falls well in the middle of the data. Average length of stay, however, equals 38.5. It falls, essentially, in the final bar of this histogram and well beyond where the majority of the data lies. The provides a visual demonstration of the impact of outliers on ALOS.
Providers should monitor both ALOS and MLOS. Significant differences between these numbers would indicate the presence of outliers and should be investigated.
Print ‘n take hospice keys
- Understanding the difference between the average (mean) and the median
hospiceKeys-meanVsMedian
Where can you find out more?






