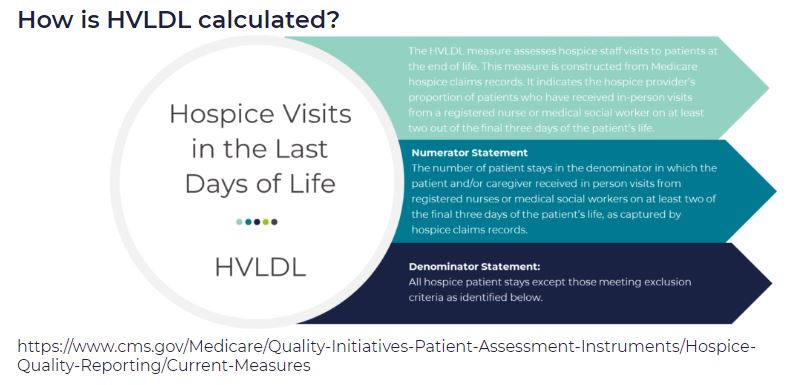
HVLDL is an HQRP claims-based measure of the proportion of patients who have received in-person visits from a registered nurse (RN) or a medical social worker (MSW) on at least two of the final three days of life. This metric replaces the HIS-based measure Hospice Visits When Death is Imminent (HVWDII).
CMS selected this metric as an important measure of quality since it is during these final days that patients most likely exhibit extreme symptoms of actively dying. This time period is also when patients most often exhibit signs of onset of clinical signs of dying. Finally, consistent visits in the final days of life are perceived as better level of care by the patient’s family.
How are the final three days of life defined?
For the purposes of HVLDL, the final three days of life are defined as:
- Day 1: day of death
- Day 2: day prior to death
- Day 3: day two days prior to death
How are days counted?
- This metric counts days, not visits
- If an RN and a MSW each visit the patient on the same day, this counts as a single day not as two visits, since the metric counts days not visits
- Telephonic visits do not count toward this metric, only in person visits
- Visits by LPN, chaplains, or other clinical staff do not count toward this metric
Which patients are included in the calculation of HVLDL?
All Medicare fee for service hospice patients are included in this metric with the following exceptions:
- Patients who did not die in hospice care
- Patients who received continuous care, respite care, or general inpatient care in the final three days of life
- Patients who were enrolled in hospice care for fewer than three days
Since HVLDL measures visits over the final three days of life, a patient must have been enrolled in hospice for at last three days to be included in the metric.
What are the data sources for this metric?
Data for HVLDL is calculated from Medicare claims data. Only data for Medicare fee for service patients who died while in hospice and who do not meet any of the exceptions listed above are included in the HVLDL calculation.
CMS calculates HVLDL using eight consecutive quarters of data. Hospice agencies with fewer than 20 “eligible patients” in the reporting period (where an “eligible patient” is defined as a patient who has died while under hospice care and does not fall under any of the exceptions listed above) are not assigned an HVLDL value. By including eight quarters of data, CMS is expanding the set of hospice agencies for which an HVLDL value will be reported. CMS will update the HVLDL value once each year.
How is the HVLDL metric calculated?
- The denominator is the count of all “eligible patients” during the reporting period
- The numerator is the count of all “eligible patients” who received an RN or MSW visit on at least two of the three final days of life
When was HVLDL introduced and where can patients and their families view the HVLDL value?
HVLDL was added to the HQRP in 2021 and began public reporting in 2022. The metric provides insight into care provided by the hospice agency in the days immediately leading up to patient death. HVLDL can be seen under the Quality of Patient Care section on the Care Compare website.
How can a hospice see its HVLDL value?
To support a hospice agency’s quality improvement efforts, CMS shares the agency’s HVLDL value in the Hospice Agency Level QM Report in CASPER. CASPER reports separately the numerator and denominator of HVLDL as well as the hospice observed percent – the agency’s HVLDL score. CASPER also reports on the national average HVLDL score and the agency’s percentile. Percentile rank indicates what percentage of agencies nationwide had a HVLDL score that was equal to or lower than the agency’s score. A hospice agency can benchmark its HVLDL score with the national average and the percentile rank. It can also trend its performance against its own HVLDL value over time.
Why did CMS replace the HIS HVWDII?
CMS implemented HVWDII in 2017. This metric measured hospice visits by non-clinical team members including LPN, chaplain, MSW, and hospice aides during the final seven days of a patient’s life. Analyzing the data collected by this metric, CMS found that HVWDII was unable to distinguish between high quality and low quality hospice agencies (i.e., it failed the CMS validity testing criteria). Consequently, CMS sought a replacement metric. The revised metric is also aligned with the Service Intensity Add-On (SIA) payment initiative (which incentivizes visits by RN and MSW near patient’s death). HVLDL has an added benefit that it is calculated based on claims data so it does not add a reporting burden for hospice agencies.
Where can you learn more?
- CMS definition of HVLDL: CMS – HVLDL
- HQRP metrics: CMS – HQRP
- HQRP HCI Score: What is Hospice Care Index (HCI)?
Image from Medalogix




0 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks